Library
In this space, we share relevant information produced by Siztema and its partners.
- 1. System, Management, and Management Systems concepts.
- 2. Management System Design Tool.
- 3. Results within a Management System.
- 4. Principles of Action of the Management System.
- 5. Execution and The Value Creation System
- 6. The Continuous Improvement System.
- 7. The Continuous Learning System.
- 8. Design of the Management System.
- 9. The Team.
- 10. Holistic Transformation.
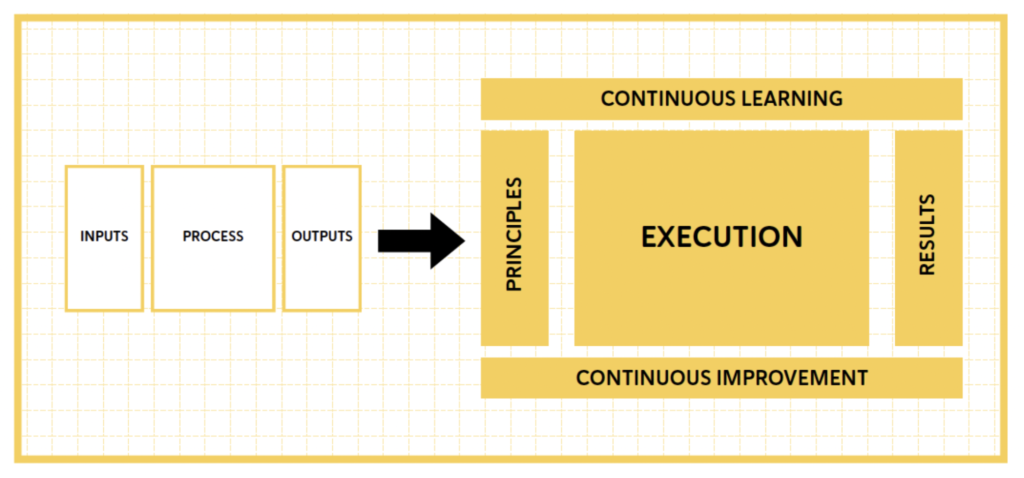
A basic Management System is made up of inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback.
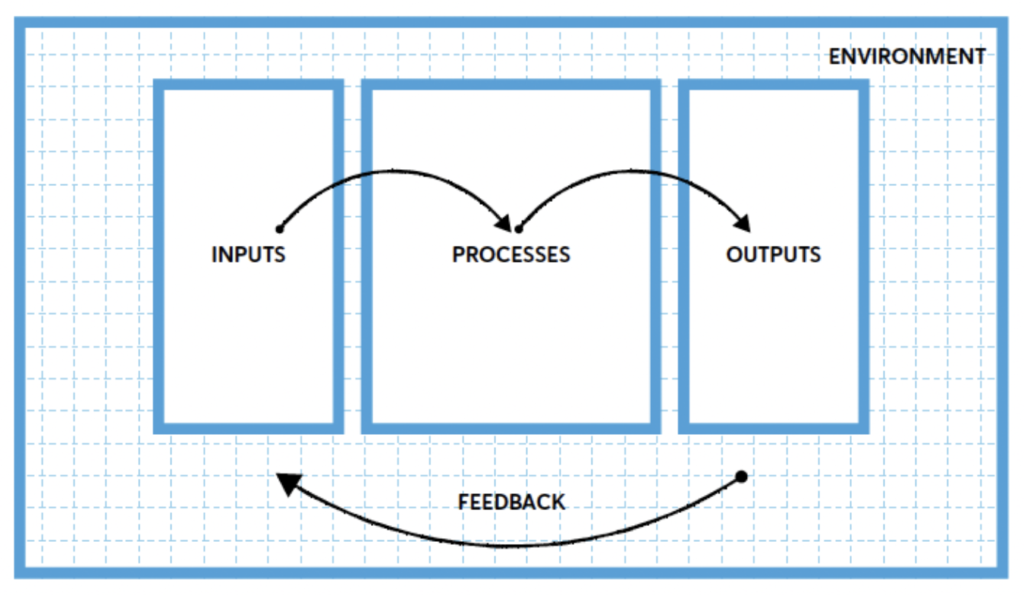
- Inputs: What goes into the system.
- Processes: The transformation of an input into an output.
- Outputs:. The results you get from processing the inputs.
- Feedback: Communicates the positive and negative so that processes, products, and services are improved.
The Management System
Is the management of an organization based on a system
Management System Design Tool
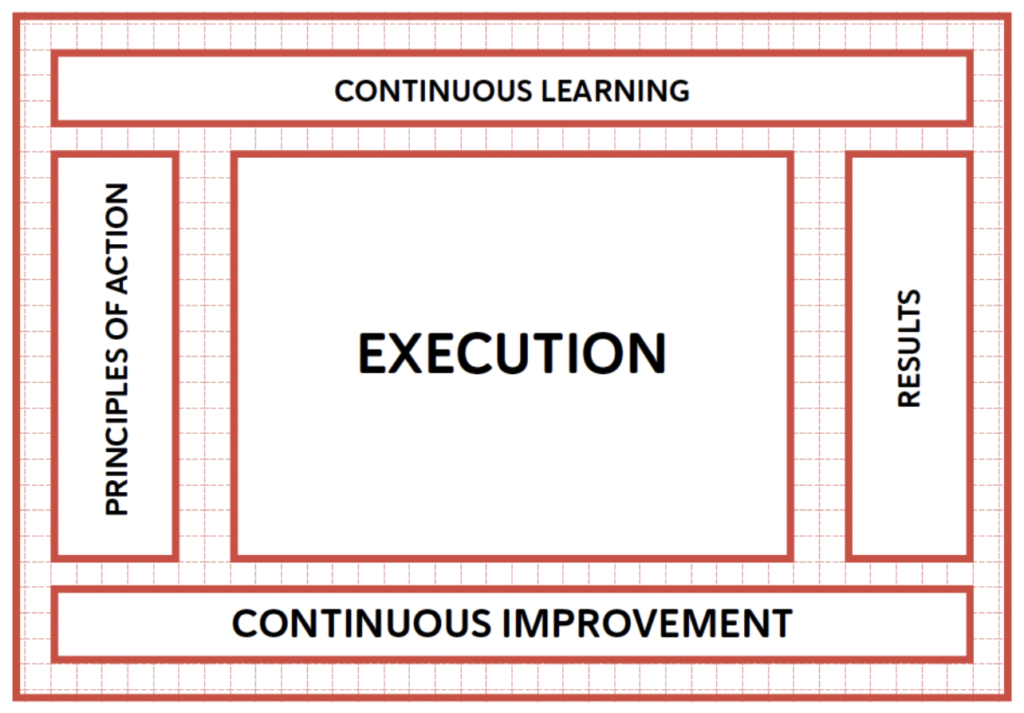

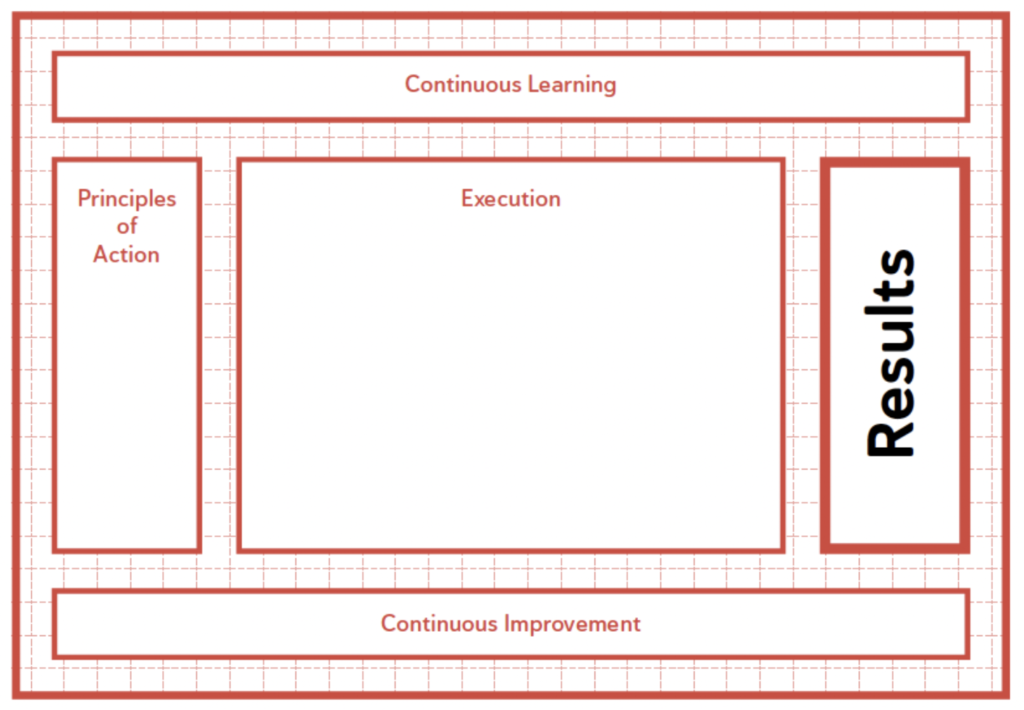
The results are the outputs of the system, what the system aims to achieve.
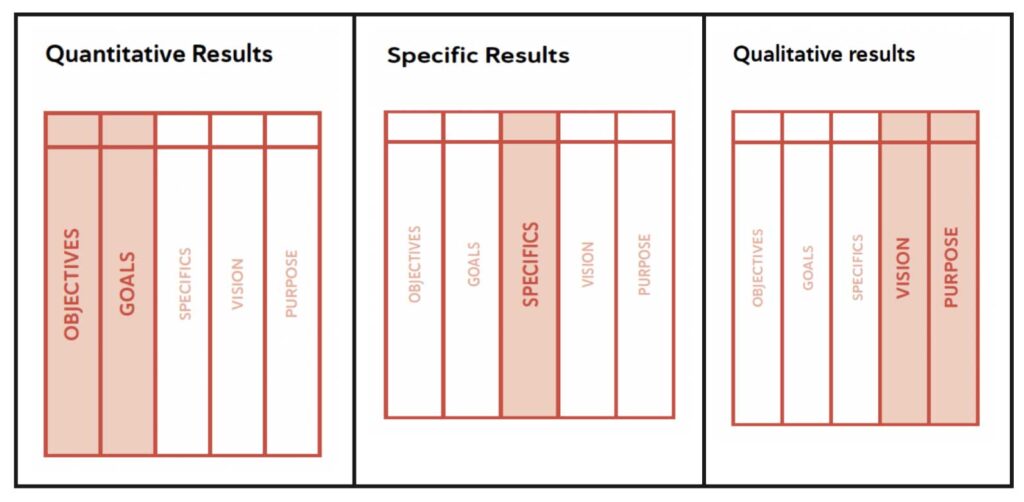
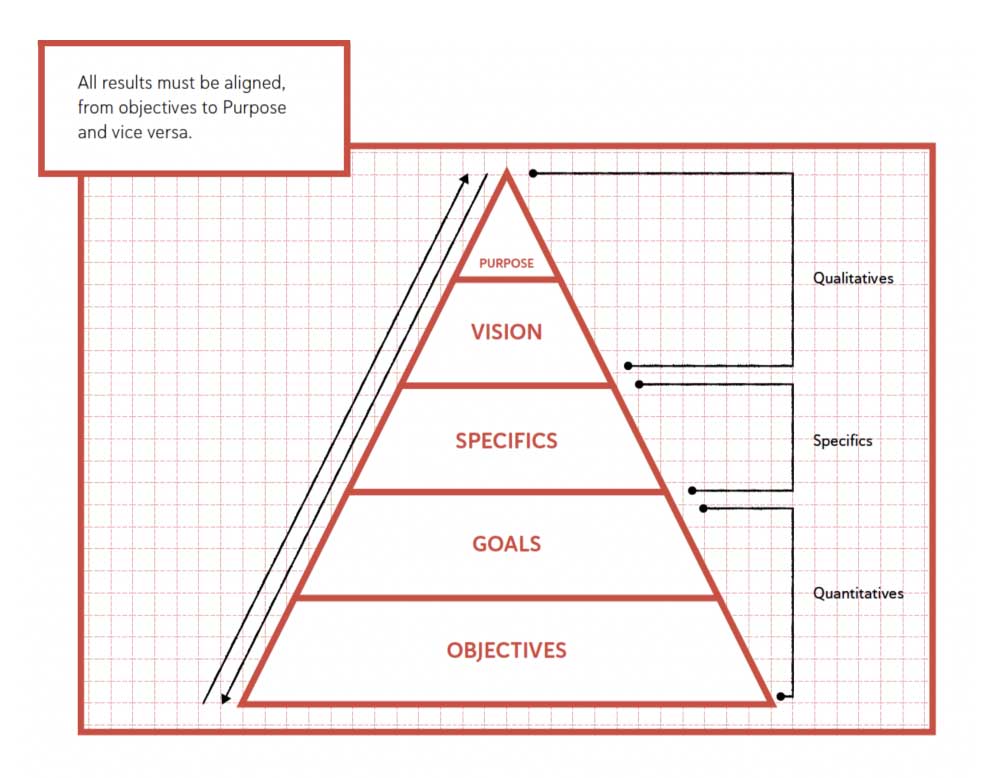
Principles are the input and support of the Management system Design Tool and should enhance the likelihood of attaining desired outcomes.
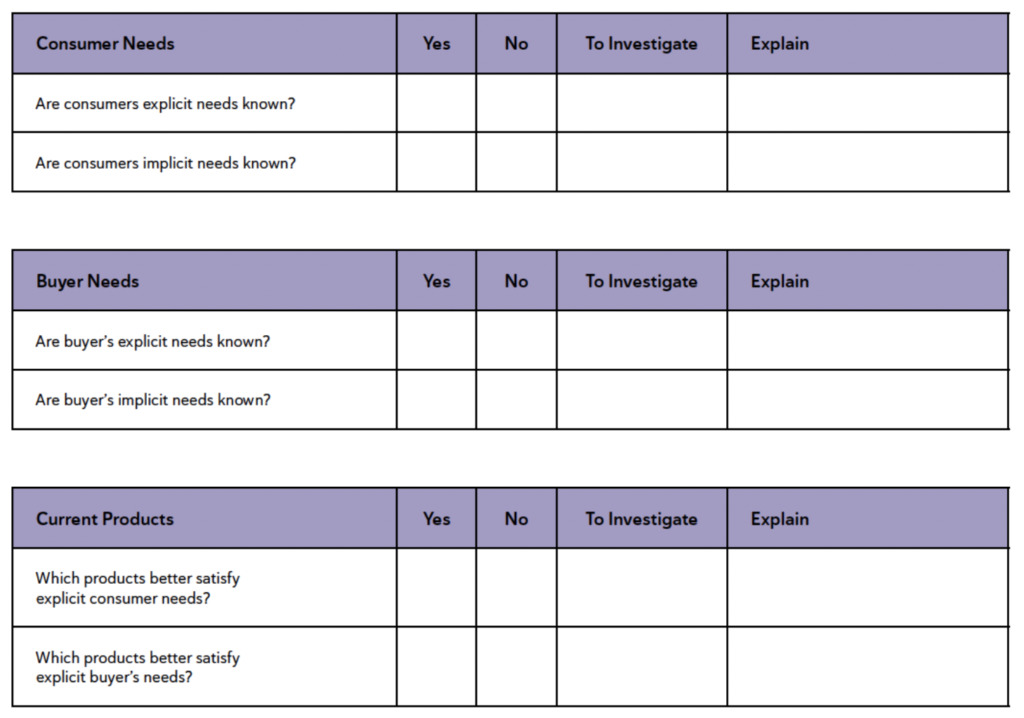
Evaluation Exercise
- Identify Existing Principles: The team starts by listing all the principles they believe are currently in place within the company.
- Categorize Principles: On the right side of a chart or page, write down the principles the team considers positive. On the left side, list the principles perceived as negative.
- Rate the Principles: Assign a score to each principle. The most positive principle receives a +5 rating, indicating strong alignment with company results. Conversely, the most negative principle gets a -5 rating, showing significant hindrance to achieving company results. Rate all other principles, accordingly, based on their perceived impact.
By conducting this exercise, a team can clearly visualize which principles are fostering success and which may
need to be re-evaluated or changed to ensure they align with the company’s intended results.

To achieve any results, a series of tasks must be performed; this is known as execution.
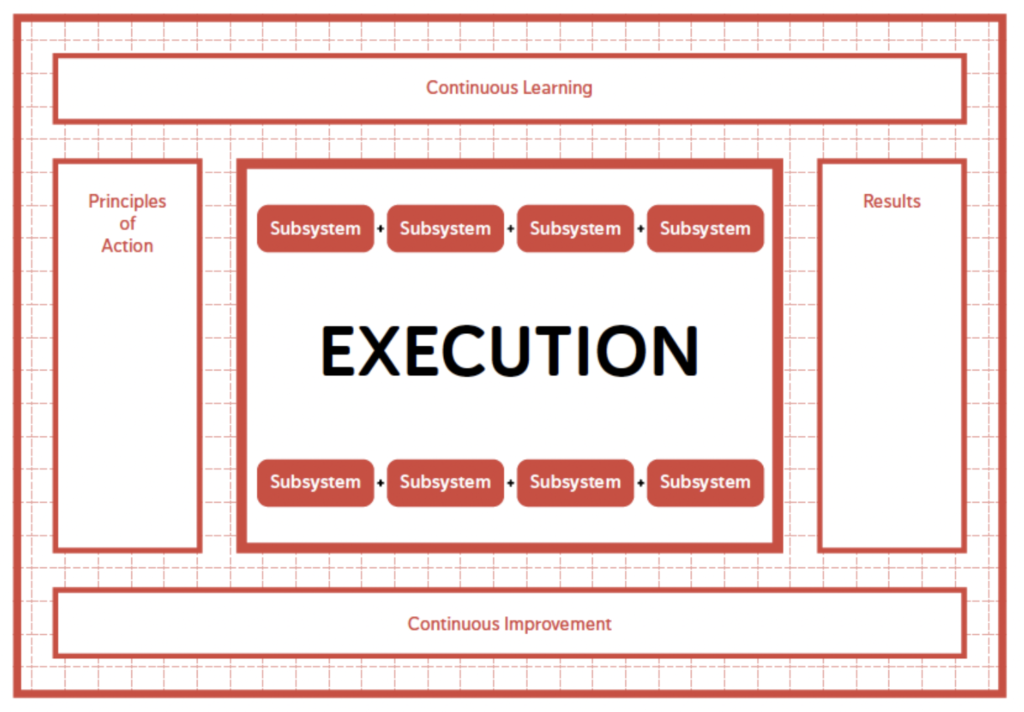
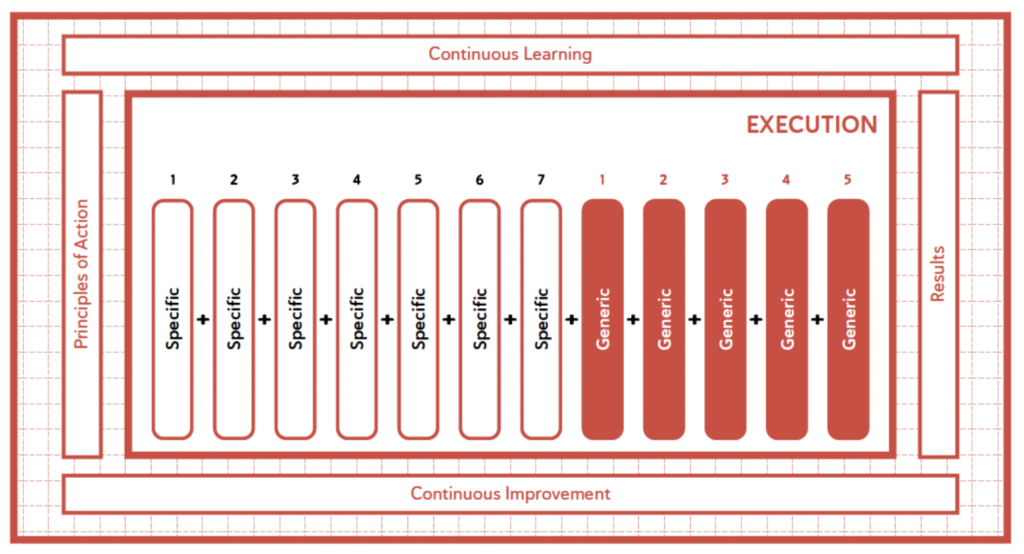
The value creation system
Good companies have teams that continuously improve within a well-designed Management System.
It is the persistent effort to acquire the knowledge and relevant skills needed to achieve the defined results.
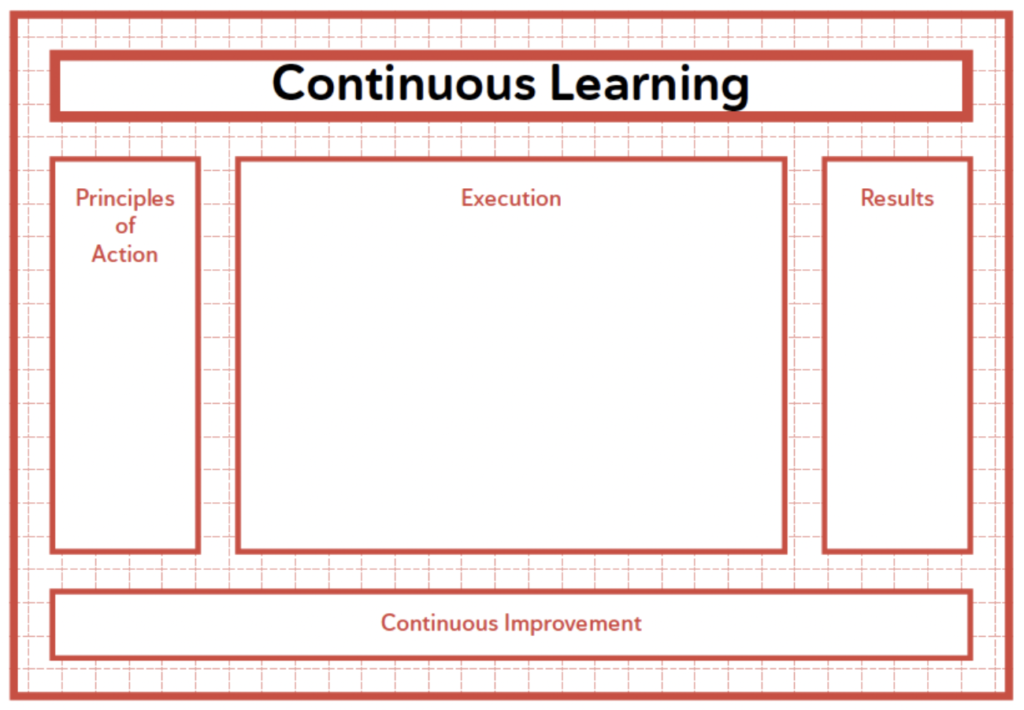
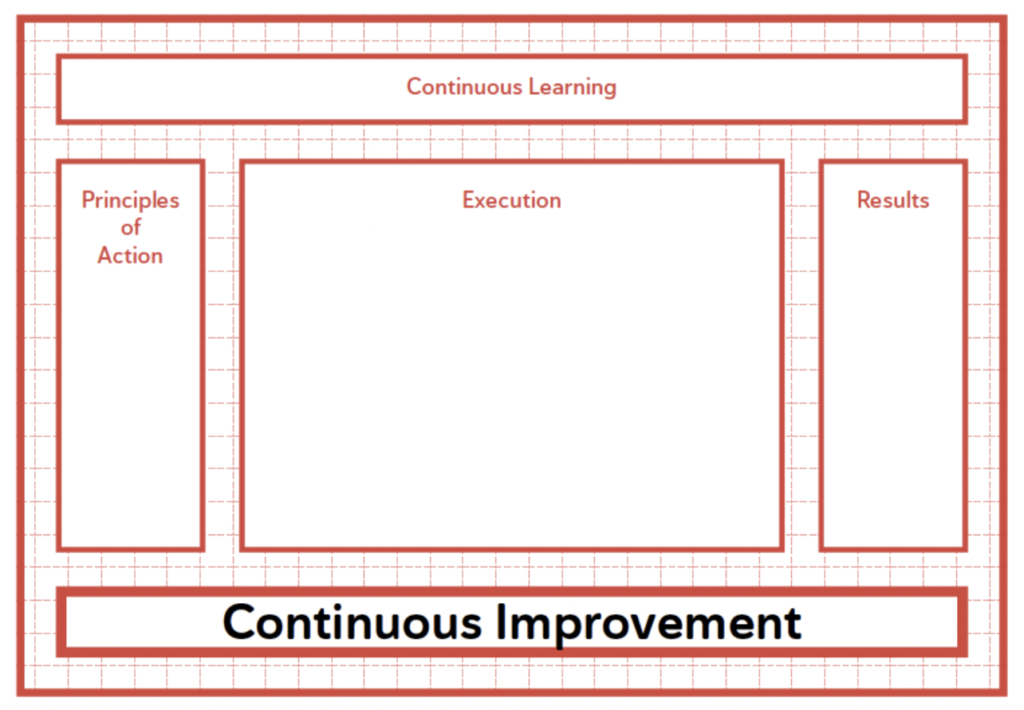
Designing the Management System entails creating and outlining a Management System focused on achieving results through various interrelated components such as principles, execution and its subsystems, Continuous Improvement, and learning.
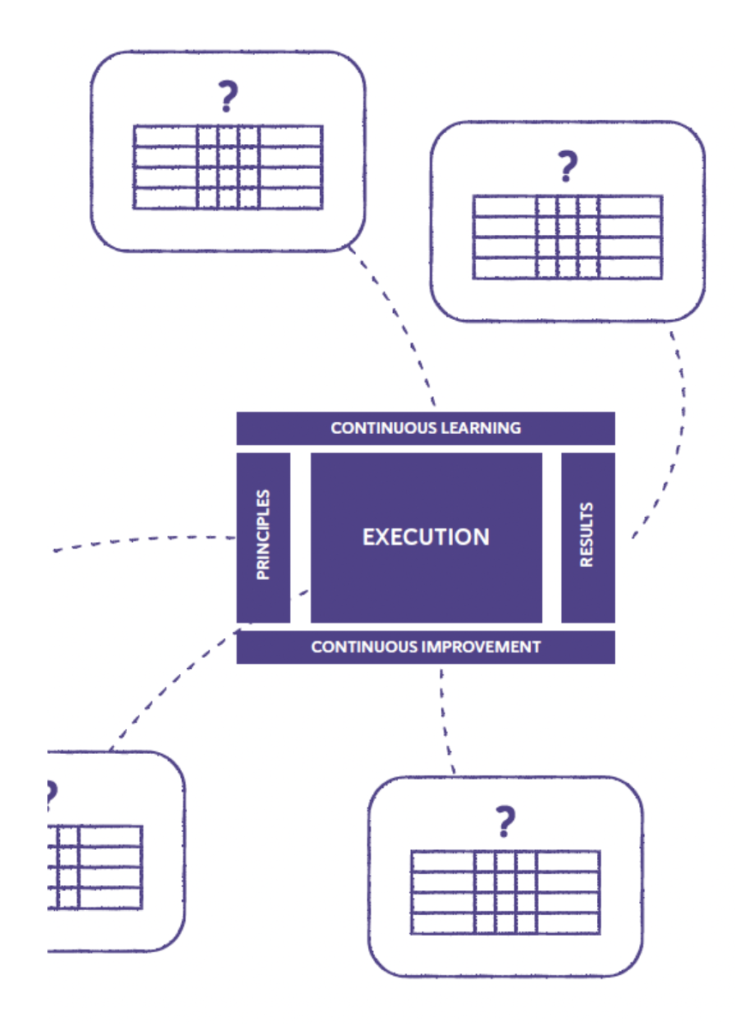
Question about the market or supra-system.
Designing with the management system tool
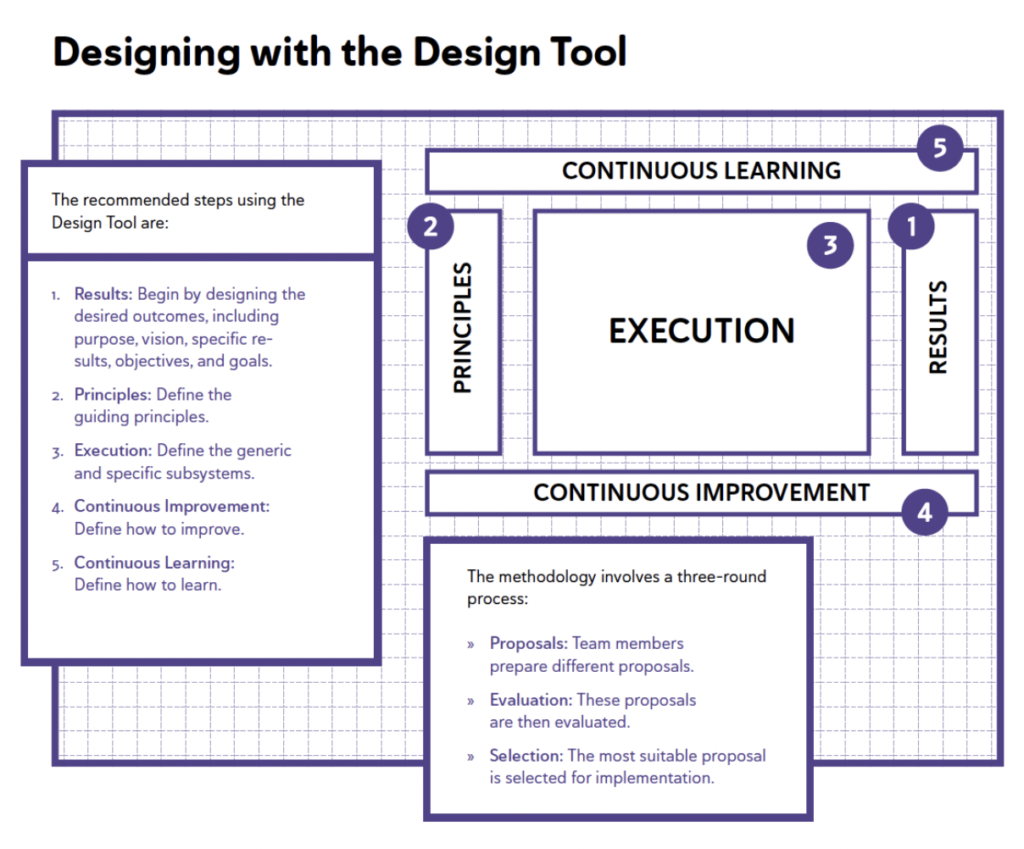

Final Design
Upon completion of the design project, a new Management System will be crafted using the Design Tool.
This new design is subject to board approval; if approved, it will move into the implementation phase.
Designing the Management System is a crucial task that keeps the company relevant in the market.

A team consists of individuals with expertise in various fields who collaborate to achieve common outcomes. United by shared principles, they are committed to execution, continuous improvement, and learning to achieve the defined results.
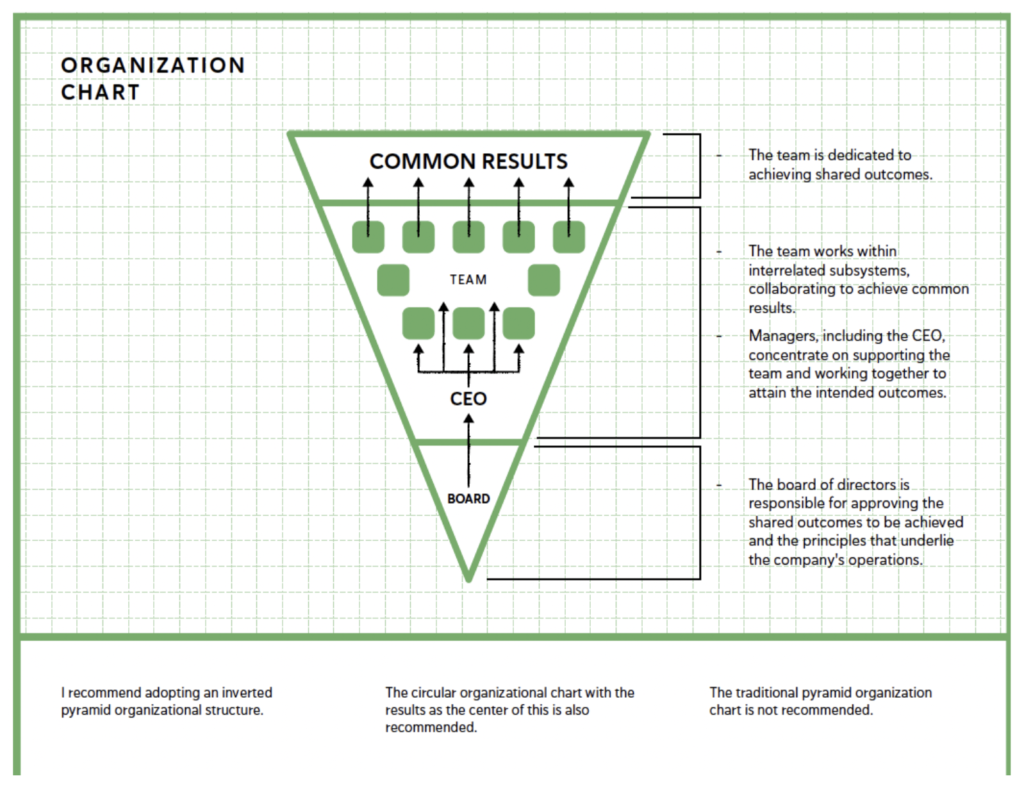
If you want to transform a company, you must first transform the Management System by which it is managed.
From a basic Management System to a new Management System
The following compares an example of a “Current Management System” with a “New Management System” designed with the Design tool.

Transformation of the Organizational Structure*
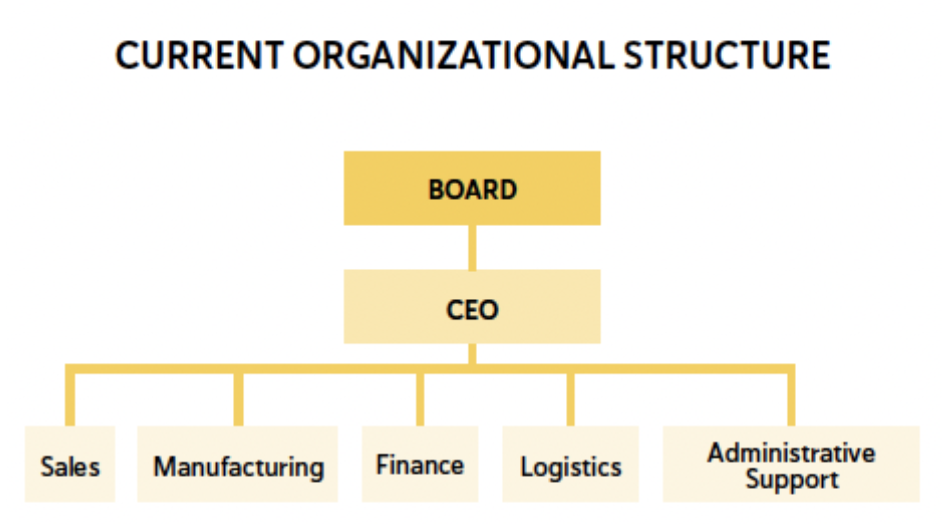
Current Organizational Structure
Traditionally, the organizational structure is designed as a pyramid, representing a power hierarchy with leaders at the top, which often leads to a top-down approach within the company. The team is dependent on this hierarchical structure.
However, this pyramidal structure dos not necessarily orient the team toward the results as outlined in the results part of the Design Tool.
* This example illustrates a company transforming its organizational structure from a top-down pyramid to a bottom-up inverted pyramid, while also defining a new Value Creation Process.
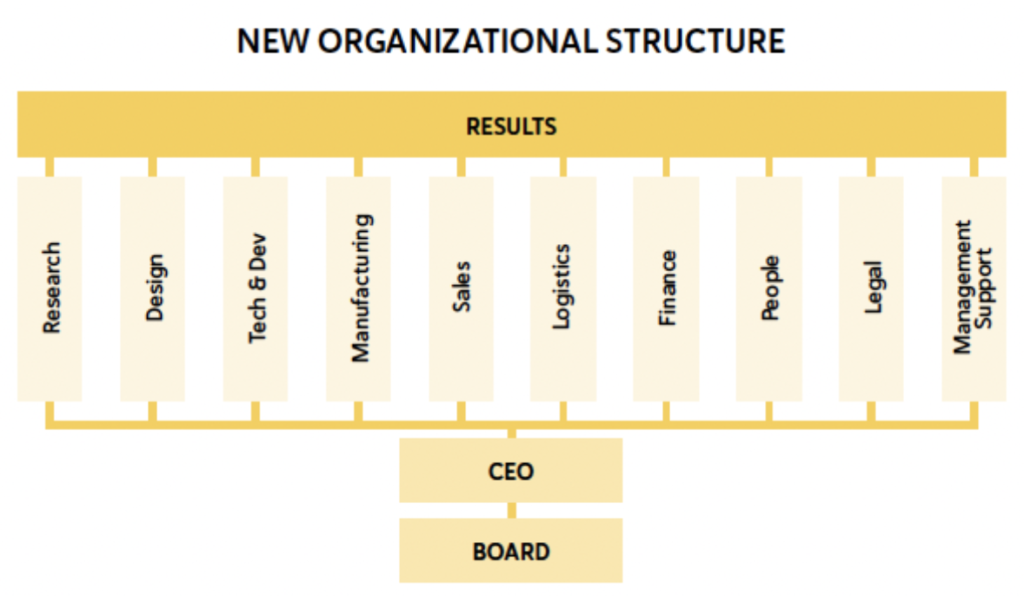
New Organizational Structure
In the new inverted pyramid organizational structure, the team’s focus within the Management System is on results rather than on individuals or a select group of people at the top.
Individuals in the highest positions are positioned at the bottom of the inverted pyramid, with their primary role being to support the rest of the team in achieving the defined results.
The Management System acts as a support structure for the team.
A basic Management System is made up of inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback.

- Inputs: What goes into the system.
- Processes: The transformation of an input into an output.
- Outputs:. The results you get from processing the inputs.
- Feedback: Communicates the positive and negative so that processes, products, and services are improved.
The Management System
Is the management of an organization based on a system
Management System Design Tool



The results are the outputs of the system, what the system aims to achieve.


Principles are the input and support of the Management system Design Tool and should enhance the likelihood of attaining desired outcomes.
Evaluation Exercise
- Identify Existing Principles: The team starts by listing all the principles they believe are currently in place within the company.
- Categorize Principles: On the right side of a chart or page, write down the principles the team considers positive. On the left side, list the principles perceived as negative.
- Rate the Principles: Assign a score to each principle. The most positive principle receives a +5 rating, indicating strong alignment with company results. Conversely, the most negative principle gets a -5 rating, showing significant hindrance to achieving company results. Rate all other principles, accordingly, based on their perceived impact.
By conducting this exercise, a team can clearly visualize which principles are fostering success and which may
need to be re-evaluated or changed to ensure they align with the company’s intended results.

To achieve any results, a series of tasks must be performed; this is known as execution.

The value creation system

Good companies have teams that continuously improve within a well-designed Management System.

It is the persistent effort to acquire the knowledge and relevant skills needed to achieve the defined results.

Designing the Management System entails creating and outlining a Management System focused on achieving results through various interrelated components such as principles, execution and its subsystems, Continuous Improvement, and learning.

Question about the market or supra-system.


Designing with the management system tool


Final Design
Upon completion of the design project, a new Management System will be crafted using the Design Tool.
This new design is subject to board approval; if approved, it will move into the implementation phase.
Designing the Management System is a crucial task that keeps the company relevant in the market.

A team consists of individuals with expertise in various fields who collaborate to achieve common outcomes. United by shared principles, they are committed to execution, continuous improvement, and learning to achieve the defined results.

If you want to transform a company, you must first transform the Management System by which it is managed.
From a basic Management System to a new Management System

The following compares an example of a “Current Management System” with a “New Management System” designed with the Design tool.

Transformation of the Organizational Structure*

Current Organizational Structure
Traditionally, the organizational structure is designed as a pyramid, representing a power hierarchy with leaders at the top, which often leads to a top-down approach within the company. The team is dependent on this hierarchical structure.
However, this pyramidal structure dos not necessarily orient the team toward the results as outlined in the results part of the Design Tool.
* This example illustrates a company transforming its organizational structure from a top-down pyramid to a bottom-up inverted pyramid, while also defining a new Value Creation Process.

New Organizational Structure
In the new inverted pyramid organizational structure, the team’s focus within the Management System is on results rather than on individuals or a select group of people at the top.
Individuals in the highest positions are positioned at the bottom of the inverted pyramid, with their primary role being to support the rest of the team in achieving the defined results.
The Management System acts as a support structure for the team.
